10_SpringBoot_启动配置原理
- 启动原理
- 运行流程
- 自动配置原理
几个重要的事件回调机制
配置在META-INF/spring.factories中:
ApplicationContextInitializer
SpringApplicationRunListener
只需要加在IOC容器中:
ApplicationRunner
CommandLineRunner

先创建一个简单的SpringBoot-web工程
断点打在启动类的main方法上进行debug
启动流程:
-
创建SpringApplication对象
initialize(sources); private void initialize(Object[] sources) { // 保存主配置类 if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) { this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources)); } // 判断当前应用是否为web应用 this.webEnvironment = deduceWebEnvironment(); // 从类路径下找到META-INF/spring.factories配置的所有ApplicationContextInitializer;然后保存起来。 setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances( ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); // 还是从类路径下找到META-INF/spring.factories配置的所有ApplicationListener setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); // 从多个配置类中找到有main方法的主配置类 this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); }把这些initializers都保存起来
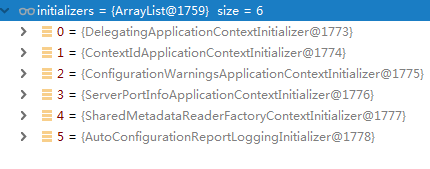
把这些listeners也保存起来
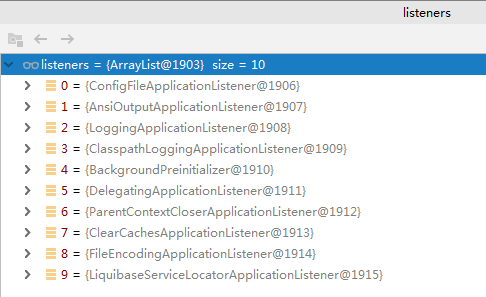
-
运行run方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { // 停止的监听 StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); // 声明一个ioc容器,指向null ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null; // 做awt有关的 configureHeadlessProperty(); // 获取SpringApplicationRunListeners,是从类路径下META-INF/spring.factories SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); // 回调所有的SpringApplicationRunListeners的starting()方法 listeners.starting(); try { // 封装命令行参数 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments( args); // 准备环境 // 1. 创建环境完成后,会回调所有SpringApplicationRunListeners的environmentPrepared()方法:表示环境准备完成 // 2. 如果是web环境还会转成web环境 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,applicationArguments); // 打印Banner图标 Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); // 创建ioc容器ApplicationContext // 1. 根据你的环境,决定创建的web环境与否,直接是利用全限定名然后用BeanUtil进行反射创建对象return回去。 context = createApplicationContext(); // 主要是用来发生异常的时候做异常分析报告的 analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context); // 准备上下文环境 // 将environment保存到ioc容器当中; // 而且调用applyInitializers();回调之前保存的所有的ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize()方法 // 还要回调所有的SpringApplicationRunListener的contextPrepared()方法; // prepareContext运行完成后,还要回调所有的SpringApplicationRunListener的contextLoaded()方法 prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); // 刷新容器:IOC容器初始化;重点关注refresh()方法的finishBeanFactoryInitialization() 创建所有的单例Bean和容器中所有的组件 // 如果是web应用还会创建嵌入式的tomcat等 // **扫描,创建,加载所有组件的地方**(配置类,组件,自动配置) refreshContext(context); // 从IOC容器中获取所有的ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner进行回调 // ApplicationRunner先回调,然后CommandLineRunner回调 afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); // 所有的SpringApplicationRunListener回调finished()方法 listeners.finished(context, null); // 监听结束 stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) { new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass) .logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } //整个SpringBoot应用启动完成以后返回启动的IOC容器 return context; } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, listeners, analyzers, ex); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } }找到的Listener:
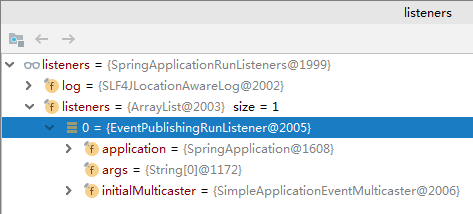
refresh方法:
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } } -
事件监听机制
配置在META-INF/spring.factories中:
ApplicationContextInitializer
SpringApplicationRunListener
只需要加在IOC容器中:
ApplicationRunner
CommandLineRunner
首先创建4个类分别实现上述几个接口,并进行实现,注意SpringApplicationRunListener需要构造器,参考别的实现即可。
ApplicationContextInitializer:
public class HelloApplicationContextInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> { @Override public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) { System.out.println("HelloApplicationContextInitializer.initialize"); System.out.println("初始化容器"+applicationContext); } }SpringApplicationRunListener:
public class HelloSpringApplicationRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener { public HelloSpringApplicationRunListener(SpringApplication application,String[] args) { System.out.println("HelloSpringApplicationRunListener.HelloSpringApplicationRunListener"); } @Override public void starting() { System.out.println("HelloSpringApplicationRunListener.starting"); } @Override public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { Object o = environment.getSystemProperties().get("os.name"); System.out.println("HelloSpringApplicationRunListener.environmentPrepared"+o); } @Override public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { System.out.println("HelloSpringApplicationRunListener.contextPrepared"); } @Override public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { System.out.println("HelloSpringApplicationRunListener.contextLoaded"); } @Override public void finished(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) { System.out.println("HelloSpringApplicationRunListener.finished"); } }ApplicationRunner:
@Component public class HelloApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner { @Override public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { System.out.println("HelloApplicationRunner.run"); } }CommandLineRunner:
@Component public class HelloCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner { @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { System.out.println("HelloCommandLineRunner.run"+ Arrays.asList(args)); } }接着在类路径下创建META-INF文件夹,里面编写一个spring.factories文件,因为ApplicationContextInitializer和SpringApplicationRunListener需要这样配置:
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\ top.tomxwd.listener.HelloApplicationContextInitializer org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\ top.tomxwd.listener.HelloSpringApplicationRunListener而ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner则需要在类上打个
@Component注解即可被扫描到。这时候启动应用,就会看到输出结果。



评论区